last update: 02/27/2007

| Functional SELEX method |
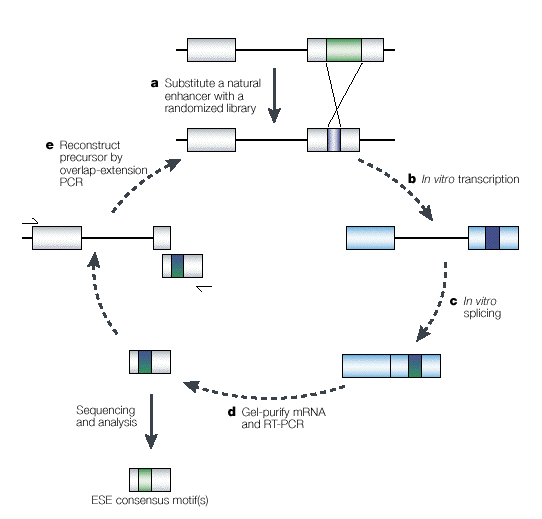
To identify exonic splicing enhancer (ESE) motifs by functional in vivo or in vitro SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment), a minigene is used that harbors ESE sequences that are required for the efficient splicing of its pre-mRNA. As shown in the accompanying figure, the natural enhancer (green box) is replaced by random sequences (blue) from an oligonucleotide library (a). The resulting pool of minigenes is then transfected into cultured cells, or is transcribed in vitro, to generate a pool of pre-mRNAs (b). Following in vivo or in vitro splicing (c), the pool of spliced mRNAs is amplified by RT-PCR and gel-purified (d). This pool of enhancer-enriched sequences is then used to reconstruct new minigene templates by overlap-extension PCR (e), to use in a new enrichment cycle. The iteration of this entire procedure yields a limited number of "winners" - sequences that possess good splicing enhancer activity. To identify ESEs that are recognized by individual SR proteins, the splicing step was carried out in S100 extract complemented with one of four different SR proteins (SF2/ASF, SC35, SRp40 and SRp55). Transcripts were derived from an IgM-derived minigene in which the natural enhancer was substituted with a pool of 20-nucleotide random sequences. After a few cycles of enrichment, spliced products were sequenced and aligned to derive a consensus motif. The frequencies of the individual nucleotides at each position were then used to calculate a score matrix (shown below), which can be used to predict the location of SR-protein-specific putative ESEs in exonic sequences. |
| Matrices & thresholds |
The current weighted matrix values (release 3.0) and the consensus motifs obtained with these four SR proteins are shown below; the height of each letter reflects the frequency of each nucleotide at a given position, after adjusting for background nucleotide composition. At each position, the nucleotides are shown from top to bottom in order of decreasing frequency; orange letters indicate above-background frequencies. (The pictogram representation method was described by Burge and colleagues (Burge, C.B.,Tuschl, T., Sharp, P.A. in The RNA world II, 525-560, CSHL press, 1999).
| Protein | Matrix | Logo | Threshold | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SF2/ASF |
|
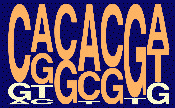 |
1.956 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SF2/ASF (IgM-BRCA1) |
|
 |
1.867 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SC35 |
|
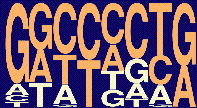 |
2.383 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SRp40 |
|
 |
2.670 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SRp55 |
|
 |
2.676 |
The above material is Copyrighted. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
The thresholds are values above which we consider a score for a given sequence to be significant (high-score motif).
Our default threshold values are set as the median of the highest score for each sequence in a set of 30 randomly-chosen 20-nt sequences (from the starting pool used for functional Selex).
The matrices for splice sites were derived from constitutive exons (data from dbCASE, database of classified alternative splicing events, unpublished) and the thresholds correspond to the first quantile of all splice site scores. The branch site matrix was derived the data generated by Kol et al. 2005, Hum Mol Genet 14: 1559-1568) and the threshold is arbitrarily set to zero.
| References |
(include some works that used the matrices).
1. Liu, H.-X., Zhang, M., and Krainer,
A.R. (1998) Identification
of functional exonic splicing enhancer motifs recognized by individual
SR proteins.Genes Dev.12: 1998-2012.
2. Liu HX, Chew SL, Cartegni L, Zhang MQ, Krainer AR. (2000)
Exonic
splicing enhancermotif recognized by human SC35 under splicing
conditions.Mol Cell Biol. 20(3):1063-71.
3. Liu HX, Cartegni L, Zhang MQ, Krainer AR. (2001) A
mechanism for exon skipping caused by nonsense or missense mutations
in BRCA1 and other genes Nat Genet.; 27(1):55-8.
4. Cartegni L, Krainer AR. (2002) Disruption of an SF2/ASF-dependent exonic splicing enhancer in SMN2 causes spinal muscular atrophy in the absence of SMN1. Nat Genet.; 4:377-84.
5. Dance GS, Sowden MP, Cartegni L, Cooper E, Krainer AR, Smith HC. (2002) Two Proteins Essential for Apolipoprotein B mRNA Editing Are Expressed from a Single Gene through Alternative Splicing. J Biol Chem; 277:12703-9.
6. Fackenthal, J.D., Cartegni, L., Krainer,
A.R., and Olopade, O.L., BRCA2
T2722R is a deleterious allele that causes exon skipping.
Am J Hum Genet, 2002. 71(3): p. 625-631.
7. Caputi, M., Kendzior, R.J., Jr., and Beemon, K.L., A
nonsense mutation in the fibrillin-1 gene of a Marfan syndrome
patient induces NMD and disrupts an exonic splicing enhancer.
Genes Dev, 2002. 16(14): p. 1754-1759.
8. Smith, P.J., Spurrell, E.L., Coakley, J., Hinds, C.J., Ross,
R.J.M., Krainer, A.R., and Chew, S.L., An Exonic Splicing Enhancer in Human IGF-I Pre-mRNA
Mediates Recognition of Alternative Exon 5 by the Serine-Arginine
Protein Splicing Factor-2/ Alternative Splicing Factor. Endocrinology, 2002. 143(1): p. 146-154.
9. Ferrari, S., Giliani, S., Insalaco,
A., Al-Ghonaium, A., Soresina, A.R., Loubser, M., Avanzini, M.A.,
Marconi, M., Badolato, R., Ugazio, A.G., Levy, Y., Catalan, N.,
Durandy, A., Tbakhi, A., Notarangelo, L.D., and Plebani, A.,
Mutations of CD40 gene cause an autosomal recessive
form of immunodeficiency with hyper IgM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2001. 98(22):
p. 12614-12619
10. Wang, J. Smith, P. J., Krainer, A. R., and Zhang, M. Q.
Distribution of SR protein exonic splicing enhancer motifs in human protein-coding genes. Nucl. Acids Res., 2005. 33(16):
p. 5053-5062
11.Smith, P. J., Zhang, C., Wang, J., Chew, S. L., Zhang, M., Q, and Krainer, A. R.
An increased specificity score matrix for the prediction of SF2/ASF-specific exonic splicing enhancers Hum. Mol. Genet. 15(16):
p. 2490-2508
12.Kol, G., Lev-Maor, G., Ast, G
Human-mouse comparative analysis reveals that branch-site plasticity contributes to splicing regulation Hum. Mol. Genet. 14(11):
p. 1559-1568
Krainer Lab and
Zhang Lab,
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, all
rights reserved
Questions/suggestions email: Jinhua Wang.